Red currant is a berry shrub common in summer cottages. Growing this culture, even novice gardeners will be easy. It can be propagated either by cuttings, lignified or green, or by vertical or horizontal layering, dividing bushes, and in other ways.
The benefits of red currants
This culture is appreciated by gardeners for resistance to frost and productivity - up to 17 kg of fruits are removed from one bush, which contain a set of vitamins C and P necessary for a person, ascorbic acid, sugars (4-11%), pectin and tannins.
Berries of red currant are consumed fresh, frozen or processed for jam, jam. Gelling properties allow the preparation of marmalade and marshmallows.

Red currant yields a very tasty jelly, which can be eaten as an independent dessert, and used in other dishes
In addition, it is a honey plant with medicinal properties: antipyretic for colds, anti-inflammatory and hemostatic effects.
Red currant is unpretentious, caring for it is simple. In order to receive a plentiful harvest every year, plantings are periodically updated.
Breeding methods
To propagate this crop, it is not necessary to buy seedlings in the store. Also, do not take planting material of unknown origin, as they say, from hand. In order to obtain seedlings for planting without extra costs, gardeners prefer to propagate currants on their own. However, experienced gardeners do not recommend using seeds for propagation: varietal traits of the crop are lost.
Propagation by lignified cuttings
In this way, for one growing season, the right amount of seedlings that have the characteristics of a parent plant is obtained. The advantages of this method are:
- An abundance of material for harvesting cuttings.
- The lack of transplantation leads to the fact that the roots are not injured, in a constant place the cuttings are easily rooted.
- Currants easily propagate vegetatively. The survival rate when propagated by cuttings is 90%.
Preparation of cuttings
The harvesting of cuttings begin in the first half of August. The movement of juices with the approach of autumn in the plant slows down, the cuttings will retain moisture and easily root. If reproduction is made later than the specified time, rooting slows down. Preparation of cuttings for planting is as follows:
- To begin with, we choose a fruiting healthy bush without visible damage by pests.
- We cut secateurs annual lignified shoots with a thickness of 6-8 mm.

Annual lignified shoots are cut with pruning shears
- We remove the leaves and divide the cut branch into pieces 20 cm long, leaving 5-6 buds on each.

With proper cutting, 20 cm long cuttings are obtained
- We make the upper section straight just above the kidney for proper shoot formation, under the lower kidney we make the section oblique, in the future this will allow the roots to better absorb moisture.
Put cuttings in water.

In water, roots form under the kidneys and between the nodes of the cuttings
- After the appearance of the roots, we proceed to planting.
Proper fit
Red currants are grown in lighted areas with sandy or medium loamy soil. Currant is a moisture-loving plant that usually grows on the banks of reservoirs and in lowlands. Bushes during planting are located at a distance of not less than one and a half meters from each other.
- Choose a place to land. We dig the soil to get rid of pest larvae. We clean the site from weeds and their roots.

Digging the soil is necessary to get rid of pests
- Fertilize with humus, compost or peat, or add fertilizing from mineral fertilizers (ammonium nitrate, superphosphate, potassium).
- Currants do not like acid soil. For deoxidation, we add lime, ash or chalk to the ground.

If the soil is too acidic for a bunch, then chalk is added before planting
- We dig on a bayonet of a shovel and abundantly water the soil.
- We are preparing a long trench with a depth of 15 cm, with gently sloping walls: the moisture will be better preserved.
- We plant cuttings at an angle of 20-30 cm, leaving 2-3 buds on the surface.

With proper planting of currant cuttings, 2-3 buds remain on the surface
- We compact the soil around the cuttings, removing air voids, after watering.
- To prevent moisture from evaporating, we mulch humus. The layer of mulch is 3-5 cm.
- Overwintered rooted cuttings in the spring are transplanted to a permanent place.

The plants will be ready for transplanting to a permanent place after successful wintering
Video: propagation of currants by cuttings
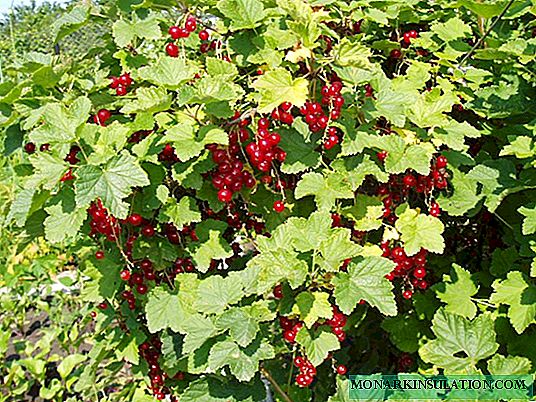
Propagation by layering
This method is used in early spring, until the buds open. Its main advantage is that the layering does not separate from the plant and does not lack water and nutrients. The disadvantage is the small amount received for planting material.
For propagation in this way, only developed annual shoots without branches are suitable.
Reproduction of currants by layering is as follows:
- Thoroughly loosen the soil around the bush, apply organic fertilizers (rotted manure) and mix thoroughly. This will help to keep more moisture in the ground and prevent crusting on the surface.
- We make grooves with a depth of 10-15 cm along the radius of the bush.
- We put the shoots in the grooves and pin them to the ground.
- Sprinkle with soil, leaving the top on the surface.
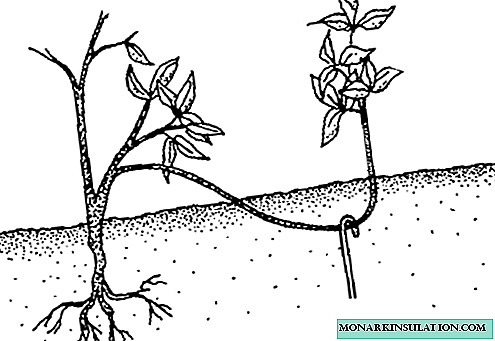
Sprouts pinned to the ground sprinkled on top of the soil
- Do not forget to water and spud during the summer.
- In the fall, having separated the rooted layers of the mother bush and dividing it into parts, we get seedlings ready for planting.
Rooting of cuttings occurs in the fall, then they are separated from the mother bush
- We dig out seedlings and plant them for growing.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
If you decide to transplant the currant bush to a new place, divide it into parts. In this way, plants ready for planting are immediately obtained. This is done in late autumn, when the growing season has ended and the plant has prepared for cold weather, or in early spring - then over the summer the seedling will have time to take root in a new place.
This method gives new bushes without special techniques and manipulations, performing simple steps:
- Choose a place to land, lit by the sun and protected from the winds.
- Thoroughly prepare the pits 60-80 cm deep: fill with humus, ash, spill with water.
- Carefully dig out the bush, trying not to damage the roots.

The bush is carefully dug up before dividing
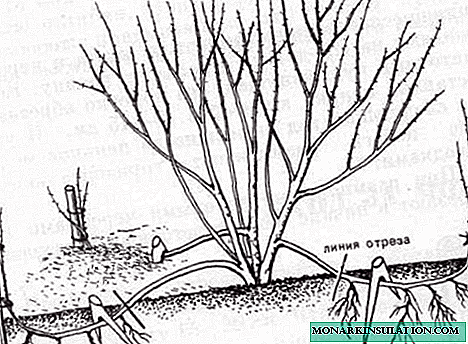
- On the bush we leave annual non-lignified branches and shorten them to 25-30 cm. We remove old branches with secateurs.
- We divide the bush into 2-3 parts, each of which has its own strong young roots and shoots.
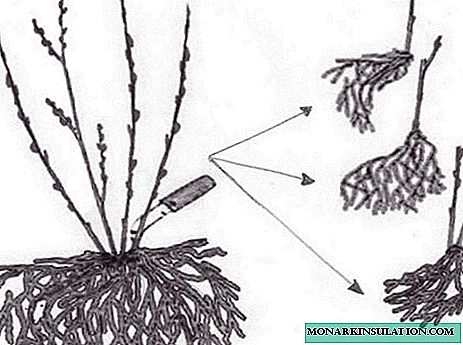
The bush is divided into 2-3 plants carefully, with a sharp knife
- We plant plants in a permanent place, not forgetting to water and spud.
In spring, new plantings will give young growth, and next year they will be pleased with the first harvest.
Propagation by green cuttings
A common way to obtain planting material using green shoots.
- At the end of May, when young shoots grow up, we cut off the tops of branches 10-15 cm long.

For reproduction, sections of branches 10-15 cm long are cut
- The upper leaves are left on the branch, the lower ones are cut off.
- Before planting, the cuttings are treated with a growth stimulator for 12-24 hours.
- In the greenhouse, we plant cuttings in the prepared soil, leaving a crown with leaves on the surface.
- To keep the plantings moist, periodically spray with water. We protect plants from direct sunlight.
- After 2-3 weeks, the cuttings will take root. We feed young plants with nitrogen fertilizers (for example, with a solution of ammonium nitrate).
- In the autumn, strong cuttings are planted in a permanent place.

New seedlings are ready for planting in the fall
Propagation by vertical layering
The branches of red currant easily break and bending to the ground is not easy. Therefore, propagation using vertical layers is used for this culture.
- In spring, we cut out a young healthy bush and leave hemp about 10 cm.
- Sprinkle the bush with damp earth - spud like potatoes.
- Periodically watering and maintaining constant humidity, we wait for the emergence of young shoots, after which we again spud.
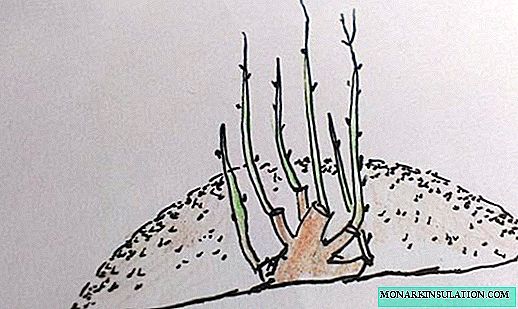
Hilling is carried out before and after the emergence of young shoots on the bush.
- In the fall, carefully secate the secateurs with rooted shoots along with the roots.
- We plant new seedlings in a permanent place.
The most effective methods of propagation of red currant are lignified cuttings and horizontal layering. Other methods are less commonly used, but each has its own advantages and disadvantages.

























